What Are Blockchain Bridges?
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we think about trust, security and value transfer. However, one of the challenges facing blockchain networks is their limited interoperability. Each blockchain network operates independently, with its own rules and protocols, making it difficult for them to communicate. This limits the possibilities for blockchain technology and hampers its potential to become a truly global, decentralized infrastructure.
Blockchain bridges offer a solution to this challenge by creating a connection between different blockchain networks. By enabling cross-chain transactions, blockchain bridges expand the possibilities of blockchain technology and facilitate the seamless transfer of value and data across different blockchain networks.
How They Enable Cross-Chain Transactions
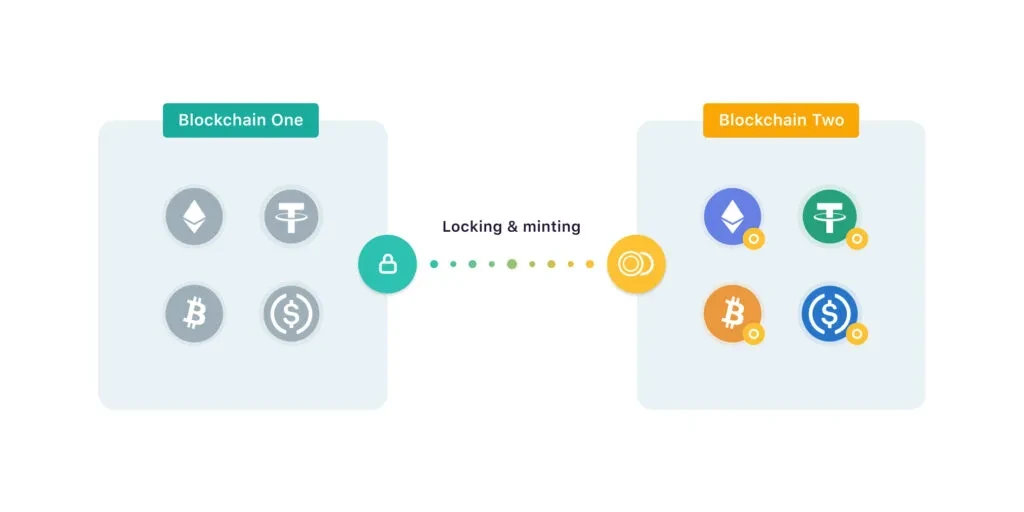
Blockchain bridges enable cross-chain transactions by creating a secure and trustless connection between two or more blockchain networks.
When a user wants to transfer a digital asset from one blockchain network to another, the asset is first locked in the original blockchain and then represented on the new blockchain using a wrapped token. A wrapped token is a token that represents another asset, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, on a different blockchain network. This wrapped token is then transferred to the destination blockchain network, where it can be redeemed for the original asset.
Smart contracts are used to facilitate these transactions, ensuring that they are executed in a secure and trustless manner. The smart contracts act as the middleman between the different blockchain networks, verifying the validity of the transactions and executing them only when certain conditions are met.
In addition to wrapped tokens, blockchain bridges also utilize sidechains and atomic swaps to enable cross-chain transactions. Sidechains are separate blockchain networks connected to the main blockchain network, allowing for the transfer of digital assets between them. Atomic swaps, on the other hand, enable the exchange of different digital assets between different blockchain networks without needing a centralized exchange.
By enabling cross-chain transactions, blockchain bridges expand the possibilities of blockchain technology, making it easier to transfer value and data between different blockchain networks. This helps to create a more interconnected and decentralized ecosystem, paving the way for a future where blockchain technology can be used to its full potential.
Types of Blockchain Bridges
Several types of blockchain bridges are used to enable cross-chain transactions between different blockchain networks. Some of the most common types of blockchain bridges include wrapped tokens, sidechains and atomic swaps.
- Wrapped Tokens: Wrapped tokens are a type of blockchain bridge that allows the transfer of assets between different blockchain networks. This is achieved by creating a token on one blockchain network representing an asset on another. For example, a Bitcoin token can be created on the Ethereum blockchain network, allowing it to be used on the Ethereum blockchain.
- Sidechains: Sidechains are another type of blockchain bridge that allows the transfer of digital assets between different blockchain networks. A sidechain is a separate blockchain network connected to the main blockchain network, allowing digital assets to be transferred between the two networks. This is achieved through a two-way peg, which enables users to move assets from the main blockchain network to the sidechain and vice versa.
- Atomic Swaps: Atomic swaps are a type of blockchain bridge that allows the exchange of different digital assets between different blockchain networks without the need for a centralized exchange. This is achieved through a smart contract, which enables two parties to exchange digital assets directly without needing a third-party intermediary.
These types of blockchain bridges offer different solutions to enable cross-chain transactions, providing users with greater flexibility and expanding the possibilities of blockchain technology.
Challenges and Risks
While blockchain bridges offer several benefits, they also have challenges and risks that must be addressed.
- Security Concerns: One of the major challenges facing blockchain bridges is security concerns. Since blockchain bridges are designed to transfer digital assets between different blockchain networks, they are vulnerable to security threats such as hacks, attacks, and other malicious activities. This is especially true for decentralized exchanges, which are more susceptible to attacks due to their decentralized nature.
- Technical Complexities: Another challenge facing blockchain bridges is technical complexities. Building a bridge between different blockchain networks is a complex process that requires a high degree of technical expertise. Moreover, since different blockchain networks have unique features and protocols, building a bridge compatible with all of them can be a significant technical challenge.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Blockchain bridges also face regulatory hurdles, as they are often subject to different regulations and laws in different jurisdictions. This can make it difficult to operate a bridge that complies with all the relevant regulations and laws, especially when operating in multiple jurisdictions.
Addressing these challenges and risks will be critical to the success of blockchain bridges in enabling cross-chain transactions and expanding the possibilities of blockchain technology.
Examples of Blockchain Bridges
There are several blockchain bridges that have been developed and deployed to enable cross-chain transactions between different blockchain networks. Some of the most notable examples include:
Polygon (formerly Matic Network)
Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC)
Polkadot
Cosmos
Polygon is a layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum that includes a blockchain bridge. The bridge allows for the transfer of assets between Ethereum and Polygon and enables developers to build decentralized applications that are compatible with both networks.
Wrapped Bitcoin is a wrapped token that represents Bitcoin on the Ethereum blockchain. This allows Bitcoin to be used on the Ethereum network, enabling users to access decentralized applications and services on both networks.
Polkadot is a multi-chain platform that includes a blockchain bridge. The bridge enables the transfer of assets and data between different blockchains connected to the Polkadot network, creating a more interconnected and interoperable ecosystem.
Cosmos is a decentralized network that includes a blockchain bridge called the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol. The IBC protocol enables the transfer of assets and data between different blockchains connected to the Cosmos network, creating a more interconnected and interoperable ecosystem.
These examples demonstrate the potential of blockchain bridges to enable cross-chain transactions and create a more interconnected and decentralized ecosystem. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, we will likely see more blockchain bridges developed and deployed to address the challenges of interoperability and expand the possibilities of blockchain technology.
Blockchain Bridges Creates a Connection Between Different Blockchain Networks
Blockchain bridges play a critical role in enabling cross-chain transactions and creating a more interconnected and interoperable blockchain ecosystem. By allowing the transfer of assets and data between different blockchain networks, blockchain bridges offer greater flexibility and expand the possibilities of blockchain technology. However, blockchain bridges also come with challenges and risks, such as security concerns, technical complexities, and regulatory hurdles, that must be addressed to ensure their success.
Despite these challenges, several notable examples of blockchain bridges already demonstrate this technology's potential. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, we will likely see more blockchain bridges developed and deployed, further expanding the possibilities of blockchain technology and enabling greater innovation in the space.
FAQs
What Is Bridging Crypto?
Bridging crypto refers to the process of enabling the transfer of digital assets or data between different blockchain networks. This is achieved through the use of blockchain bridges, which are designed to connect different blockchain networks and enable cross-chain transactions.
What Are the Best Crypto Bridges?
There are several blockchain bridges that are widely used in the crypto industry, including Polygon, Polkadot, Cosmos, and Wrapped Bitcoin. However, the best crypto bridge for a particular use case may depend on factors such as the type of assets being transferred, the blockchain networks involved, and the required level of security.
Is Bridging Crypto Safe?
Bridging crypto can be safe, but it also comes with some risks and security concerns. Since blockchain bridges are designed to transfer digital assets or data between different blockchain networks, they are vulnerable to various security threats, such as hacks, attacks, and other malicious activities. However, if proper security measures are implemented and followed, the risks of using a blockchain bridge can be mitigated.
What Are the Different Types of Crypto Bridges?
There are several types of crypto bridges, including wrapped tokens, sidechains, and atomic swaps. Wrapped tokens are tokens that represent assets on another blockchain network. Sidechains are separate blockchain networks connected to the main blockchain network, allowing digital assets to be transferred between the two networks. Atomic swaps enable the exchange of different digital assets between different blockchain networks without the need for a centralized exchange.
How Do Crypto Bridges Make Money?
Crypto bridges typically make money by charging fees for the use of their services. For example, a blockchain bridge may charge a fee for transferring digital assets between different blockchain networks. Additionally, some crypto bridges may also earn revenue from other sources, such as staking or providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges.
© 2025 OKX TR. This article may be reproduced or distributed in its entirety, or excerpts of 100 words or less of this article may be used, provided such use is non-commercial. Any reproduction or distribution of the entire article must also prominently state:"This article is © 2025 OKX TR and is used with permission." Permitted excerpts must cite to the name of the article and include attribution, for example "Article Name, [author name if applicable], © 2025 OKX TR." Some content may be generated or assisted by artificial intelligence (AI) tools. No derivative works or other uses of this article are permitted.